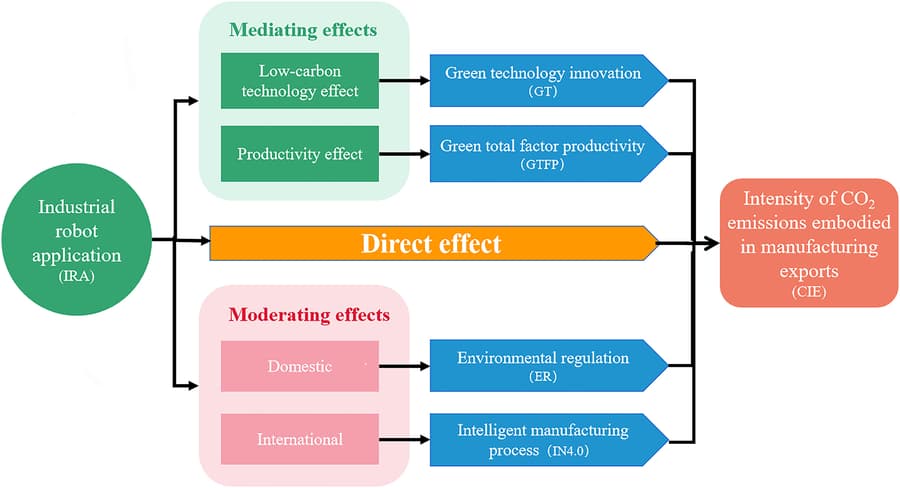
Industrial robots are emerging as a promising solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with manufacturing exports, according to a recent study published in Data Science and Management. The research, conducted by scientists from Jiangsu University and Shaoxing University, analyzed panel data from 37 countries over two decades to assess the impact of industrial robot application (IRA) on CO2 emissions embodied in manufacturing exports (CIE).
The study's findings reveal a significant reduction in CIE due to the implementation of industrial robots, demonstrating the potential of robotic automation to lower the carbon intensity of exported goods. However, the researchers also identified a U-shaped relationship between IRA and emissions, indicating that while robots initially decrease emissions, this effect eventually plateaus and may even reverse.
Dr. Xiaoli Wu, the study's corresponding author, emphasized the importance of these findings: "Integrating industrial robots into manufacturing processes is not just a technological upgrade—it's a crucial step towards realizing global sustainability goals." The research underscores that the effectiveness of industrial robots in reducing CO2 emissions is influenced by advancements in low-carbon technologies, productivity improvements, and the presence of robust environmental regulations.
The study's results have significant implications for both policymakers and industry leaders. It highlights the need for policies that support the development and adoption of industrial robots while simultaneously fostering green technological innovation. The research suggests that incorporating smart manufacturing practices and adhering to stringent environmental standards can maximize the emission-reduction potential of industrial robots.
Notably, the impact of IRA varies across different sectors, with medium-tech industries experiencing the most substantial reductions in emissions. This finding indicates that targeted implementation of robotic automation in specific industries could yield the most significant environmental benefits.
The study's nuanced approach reveals that while automation presents opportunities for greener trade, its long-term sustainability depends on how it is integrated into broader manufacturing processes. This insight is crucial for developing effective strategies to reduce the carbon footprint of global trade.
As nations worldwide grapple with the challenge of addressing climate change, this research provides valuable guidance on leveraging industrial automation to mitigate the environmental impact of manufacturing exports. By promoting strategies that combine technological advancement with sustainability initiatives, manufacturers can contribute to steering global trade towards a more eco-friendly future.
The implications of this study extend beyond the manufacturing sector, potentially influencing international trade policies and environmental regulations. As countries seek to balance economic growth with environmental responsibility, the insights provided by this research could inform the development of more effective climate change mitigation strategies.
Furthermore, the study's findings may accelerate the adoption of industrial robots and smart manufacturing practices across various industries. This could lead to a significant transformation in global manufacturing processes, with far-reaching consequences for employment, productivity, and environmental sustainability.
As the world continues to grapple with the urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, this research offers a promising avenue for achieving meaningful reductions in the carbon intensity of global trade. By highlighting the potential of industrial robots to contribute to sustainability goals, the study paves the way for a new era of green manufacturing that could play a crucial role in combating climate change.